![Best Mobile App Monetization Strategies in 2022 [Unique Guide]](https://www.codefuel.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/09/app-monetization.jpg)
Best Mobile App Monetization Strategies in 2022 [Unique Guide]
Congrats, you developed a new app for your business. You can increase the ROI of your application by monetizing. In this How to Monetize Mobile Apps – The Essential Guide, we, at CodeFuel, will walk you through all you need to know to monetize your apps successfully.
In this post
How do you monetize an app?
When you create an app, besides providing a solution, your main goal is to make money from it. So where do you start? There are several methods you can use to generate income from your application, also called app monetization.
The obvious, but the least popular, is simply charging for your app. Charging users a fee to download your application may seem a good idea, but you must consider that over 90% of applications in the Google Play Store and the Apple Store are free.
Other methods include getting paid for displaying ads within the application, getting sponsorships to promote other companies’ products, and in-app purchases, which we’ll explain in the next sections.
What Is App Monetization?
It is the process of generating revenue from your app. When publishers offer free apps, they generate revenue in other ways.
Developers need to generate revenue from their apps, but it can be challenging to stay afloat without a solid amount of funding. With most apps free to install, developers need to adjust their revenue model to generate cash after the user downloads the app. While coming up with your business model, you need to ensure that your app generates revenue and provides a great user experience.
The Mobile Apps Market
From banking to gaming and dating, we use mobile apps for our everyday needs on our smartphones. In recent years, the mobile apps market has increased exponentially. Here are some statistics:
Number of mobile app downloads worldwide in 2022 255B
Global consumer spending on mobile apps in 2019 $167B
News apps had the largest retention rate at 11% in the 3rd quarter of 2022
Apps that are used only once in 2023 25%
Most popular U.S mobile app monetization strategy in 2023 Advertising
Total consumer spending on mobile apps in the 3rd quarter 2022 $167 billion
Number of apps available in the Google Play Store 3.55M
Number of apps available in the Apple App Store 2.09M
What can we learn from this?
While in recent years advertising was the most popular monetization strategy, by the end of 2019 and 2020, subscription was the most popular app monetization model. Subscription and pay monthly models work for giants like Netflix and Spotify. In the next section, we will look into these points as we explore the different app monetization strategies.
How Mobile App Advertising Works
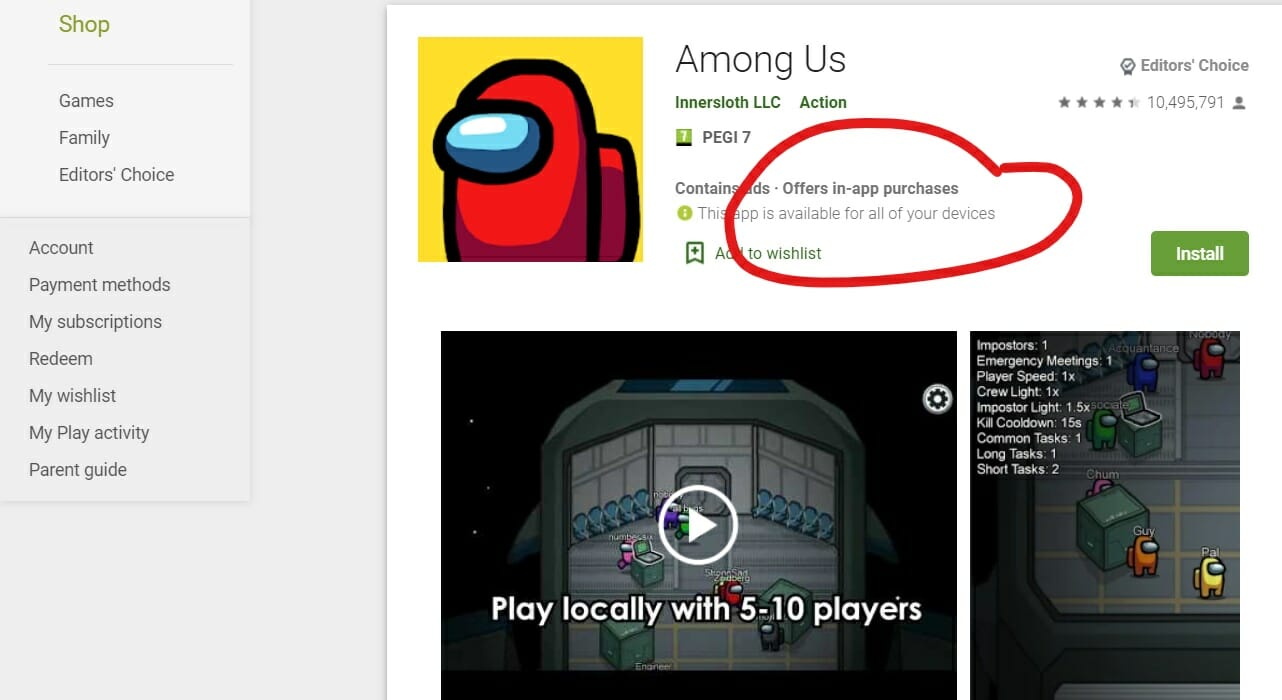
One of the most popular ways to monetize a mobile application is by adding ads to it. Mobile app advertising allows you to make money from an app without actually charging for the app. When a user downloads your app, it will present your user with ads. Every time the ads get viewed or clicked via your app, you get paid a fee.
That works because people prefer not to pay for the apps they download. No matter how cheap the app is, if there is a free alternative that works, chances are the user will prefer it. That’s why, according to Statista, 96.7% of apps in the Google Play Store in January 2021 were free.
How do you get paid? There are two metrics you should know:
- CPC: Cost per click. It means the amount the advertiser pays for each click on their ads.
- CPM: Cost per mille (thousand impressions). With this system, the advertisers set the price they will pay per 1000 ad impressions. As a developer or publisher, you’ll get paid every time a CPM ad is served to your app, and a user views it.
In the Google Play Store, CPM ads and CPC ads compete against each other. Google displays the ads that earn more revenue for you.
11 App Monetization Models and Strategies
When you plan to launch an app, monetization needs to be more than an afterthought. You should plan how your app will make money from the beginning of the project. There are many app monetization strategies applicable according to the type of app and audience. Some companies focus on one approach, while others use a combination of methods. Let’s explore:
1. Freemium – In-App Purchases
This strategy allows the user to download the app for free, but some premium features are behind a paywall. The users can try the app in the basic format, but if they want multiplayer, for example, they need to purchase the premium version. This approach can increase the audience reach and the number of downloads. Gamers can buy accessories for their characters, resources, or premium packages.
2. In-App Advertising
In-app adverts are ads that appear when a person uses the app. It seems simple, but each application implements in-app advertising in a different way. Like with every monetization strategy, it has pros and cons. On the one hand, it is easy to implement. But on the other side, too many ads can annoy the users.
How does in-app advertising work? Unlike mobile web ads, in-app advertisements appear within a mobile app. They can be banners, video ads, or display ads. Because of the large amount of time people spend on their phones, using their preferred apps, in-app advertising has a higher response among users.
What are the most common Ad Formats?
- Banner Ads: they are usually so small on a mobile screen that they don’t provide a lot of value for the advertiser.
- Interstitial Ads: they are often served at the end of a section or flow on a game. Also, when the app is loading.
- Native Ads: these types of ads integrate seamlessly into the app. Therefore, they have a higher engagement rate.
- Affiliate Ads: these generate commission from other applications by advertising them through your app.
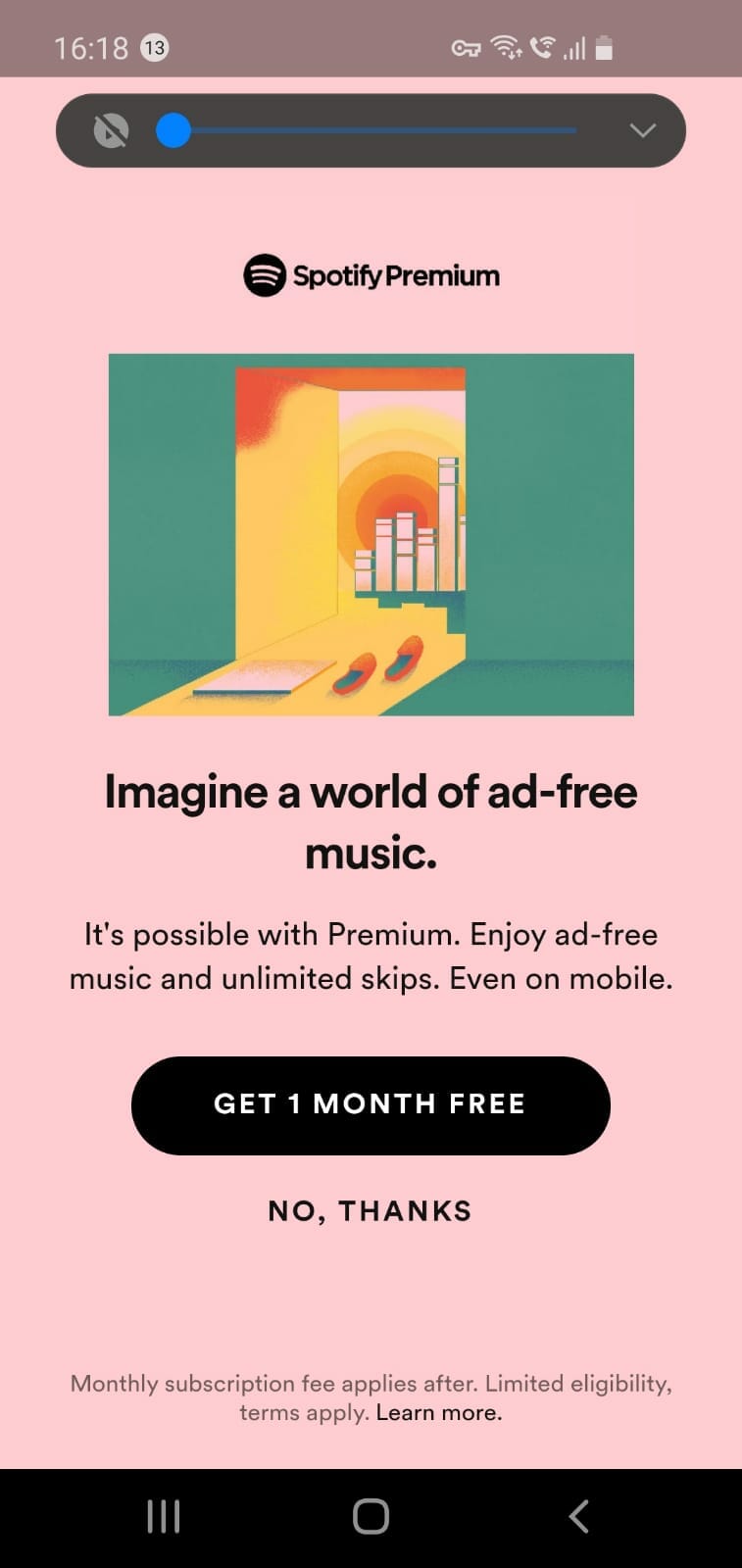
3. Upgrade to Remove Ads
In this model, ads are served unless the user pays the subscription to remove them. Spotify and YouTube music use this model.
4. Smart Installers
Ensuring your users install the app seamlessly is part of providing a great user experience. You can also earn some revenue by using a smart installer and display third-party ads. Keep the offers related to what our app offers to give more value to users.
5. Bundle Deals
Combining several utilities or extensions can be a way to give more value to your audience and increase your application’s exposure. Bundles generally attract users to perceive that they are getting a good deal, and they are more likely to buy the app.
6. Search Monetization
A search monetization strategy, such as CodeFuel, earns money by adding search capabilities to your app. Every time a user performs a search from a third-party search box, your app pulls the results from other services, and your app gets paid.
7. Pay-to-Download Apps (or Paid Apps)
In this model, developers and software publishers simply charge users for downloading the product. Publishers usually combine this model with a freemium trial period or ads. This is one of the least popular strategies because users now don’t want to pay for an app when there are many free others.
8. Affiliate marketing
Can you apply affiliate marketing for a model application? Sure, this strategy allows the app to deliver value to the end-user with coupons, season deals of other brands. This commission-based sales method involves reselling services through affiliate programs in the app.
9. Merchandise
You can use your apps as a sales channel for your own goods or services. For example, a restaurant can use an app to sell delivery orders. An online store can use a mobile app to extend its reach, offer deals and special sales.
10. Transaction fees
Your app can be a platform to sell other people’s goods and services. Uber and Airbnb use this model where they get a commission fee for their services.
11. Freemium/ Subscription service
Subscriptions are very popular as a way to generate app revenue. This model still lets the user download the app for free. They get access to all the features of the app for a trial period. Once this trial is over, they need to subscribe to keep using the app. This model is used by Netflix, Amazon Prime, almost all VPNs, and many other categories.
Best Practices to Improve App Monetization
When monetizing our app, there are some tips that can improve the strategies you implement:
- Measure user engagement – user engagement rate is one of the best metrics you can use to track your app’s chances of getting monetized. If user engagement is high, it means users are satisfied. Also, the more time the user spends in the app, the more likely they will purchase.
- Create loyalty with perks and discounts – reward loyal customers with discounts and perks. Some users may not feel comfortable with in-app purchases, but when offered a discount, may convert them.
- Build a community – some apps like mobile games thrive with communities. Players are more engaged and tend to make more in-app purchases when belonging to a community. But this practice doesn’t work only with gaming apps, cooking apps,
Ways to monetize an app
1. Search Ads
Search ads can catch your audience’s attention about your app and remind existing users to use your application. These ads appear whenever a user searches similar keywords or categories. Moreover, you can create ads in the Google Ad Network that only appear to users who already have your app.
2. Social Media Ads
Promote your app on social media through ads that link directly from sponsored Facebook posts into your app. You can do this on Facebook and Twitter.
3. Push Notifications
Catch the attention of your audience when they are not using your app. For example, have your app send notifications based on location triggers. Or send your users regular reminders with valuable and relevant content from the app.
4. Recommendation engines
Use your app with a recommendation engine to suggest related products and services that the user may want. The recommendation engine algorithm can determine exactly which offers to promote, and you profit from the clicks and referrals.
5. Promote cross-platform
You can list your application not only in Google Play and Apple Store; there are other directories and app stores outside the US that can also offer revenue. Who knows? Your app might be a success in Europe.
How to measure app success
Companies generally measure an app’s success by tracking general performance indicators like the number of mobile downloads, the number of subscriptions, the retention rate, active users, and so on. Yet, the number of downloads is not the only metric to monitor your app’s success. After all, you need to know if your app is generating revenue.
App Monetization Metrics You Should Know
Stats and Figures About App Monetization
Here are the top 5 stats and figures you must know about app monetization in 2021.
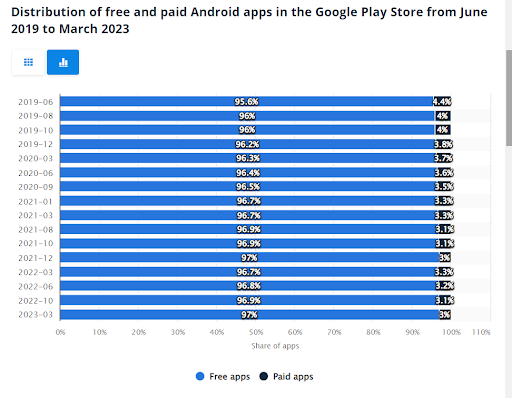
1. Distribution of free and paid Android apps in the Google Play Store 2023
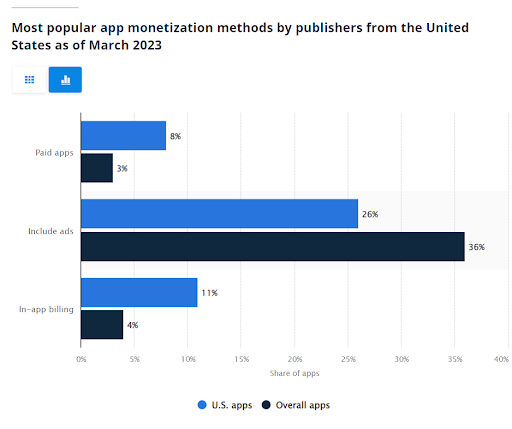
2. Mobile app popular business models
Source: Statista
3. The biggest app stores in the world:
Average in-app spend per user, per app
Average app price
What can we learn from them?
Free downloading is still the preferred way for users to try an app. Most apps in the app stores are free, so developers need to find other monetization options. From them, subscription models are the most successful. Even when you charge for your app, keep it low priced, as most applications are under $5 in the app stores.
What Does the Future Hold for Monetizing and Promoting Apps?
There is no doubt that the global mobile market is growing. According to Allied Market Research, it is expected to grow over $400 billion by 2026. From the report, we can identify the three biggest trends for app monetization for 2021 and beyond:
- Targeted advertising: personalization is one of the biggest trends of the last years. Relevant ads provide the highest engagement. Therefore, most mobile apps use AI algorithms and services that help them show relevant advertising.
- Subscription is becoming the new normal. Netflix, Prime Video, and gaming apps are leading the trend with the subscription model and upgrades.
- Virtual merchandise: In-app purchases of upgrades and packages in mobile games.
How CodeFuel Helps Companies to Monetize their Mobile Apps
CodeFuel is a complete solution that lets you leverage search, ads, shopping, and news to monetize your mobile app. By adding user intent search, you can enhance mobile applications and increase revenue.
Ready to increase your app revenue? Learn more about how CodeFuel can help.
FAQs About App Monetization
How do you monetize your mobile app?
Use the strategies mentioned in this article, like in-app purchases, freemium/premium versions, in-app advertising, and more.
How do I monetize my app with ads?
You can use affiliate ads that allow your app to generate commission from other apps by advertising them in your app. You can also display relevant native ads by using search or shopping ads engines like CodeFuel.
How do I monetize apps without ads?
You can offer premium paid features or a paid version of your app. Subscriptions and app referral programs also allow you to make money without apps,