Google Shopping Ads 101 – A Beginner’s Guide + Alternatives
Product ads are everywhere and for a reason. They bring results and continue to see growth year after year. Using shopping campaigns now is a standard advertising strategy. They drive additional revenue and increase the brand’s presence on the web.
Google Shopping Ads are the most popular, but there are alternatives, like Bing Shopping that can bring you straight to your intended market.
In this post, I’ll walk you through the basics of Google and Bing Shopping ads as well as tips to implement a successful shopping ads strategy.
In this post
What are shopping ads?
Shopping ads are a type of advertising that includes product information like an image, price, and merchant name to promote a product. The ads can be created by using product information that you submit to your ad platform. For instance, Google or Bing. This type of ad shows when a user is searching for a specific keyword.
For example, let’s say you’re looking for succulent plants to decorate your living room. As soon as you type, I’ll be getting different product images together with the product title, price, store name, and reviews. These ads give you information about potential products that may interest you.

The difference between search ads and shopping ads is that the latter display detailed information that encourages purchase, such as product title, price, store name, or reviews even before they visit the online store.
6 Benefits of Shopping Ads
1. More reach
Unlike common assumptions, Google Shopping ads are not limited to Google’s SERP. The platform increased the number of channels where they display shopping ads. That means you can reach more potential customers. Examples of where you can find Google Shopping ads include the shopping tab on Google Search, Google Images, Search Partner websites, YouTube, Gmail, and other members of Google Display Network.
2. Increased ROI
Investing in shopping ads is a smart move for your marketing strategy. Shopping ads perform better both in terms of click-through rate ( CTR), cost-per-click (CPC), and conversions. Let’s see some numbers:
- A recent report showed that users are twice more likely to click on Google Shopping Ads than on text ads.
- Another study on ad performance showed that campaigns that use shopping ads have lower CPC ($0.66 vs $1) than search ads.
- Research by Merkle advertising showed that shopping ads have a 30% more conversion rate.
These ads are more effective in bringing traffic and sales, thus resulting in better ROI. By displaying a lot of information, these ads simplify the entire customer journey.
3. Attract more attention
Shopping ads help your products get the most visibility because naturally, images drive more attention than text. Secondly, did you notice shopping ads tend to be at the top of the result page? That’s on purpose! This makes it easier to catch the attention of potential customers.
Let’s imagine you are looking to buy some women’s boots for the upcoming winter season. When you search for that in Google, your results will look something like this:
Ads with images stand out more than text ads
The images just pop off the page, right? They draw the eye immediately, that’s why shopping ads need to look attractive on search results pages so viewers are more inclined to click.
4. Better quality traffic
The ads are shown to people with a higher customer intent since they are looking for the products you are displaying. What’s more, many people searching for products on a search engine like Google already decided to buy the product. So if the search shows relevant ads like yours, the customer may find exactly what they are looking for.
5. Easy to set up and manage
Google Shopping campaigns are popular because their setup and management are really easy. To set up a shopping campaign is a simple and automated process done in the Google Merchant Center.
You don’t need to add the information about each product manually. They are tools that can pull the data from your store to generate your ads. You can also set priorities for the campaign. For instance, if a Google search calls multiple ads from your feed, the platform will show the prioritized products, for example, the ones on promotion.
6. Easy to track performance
Google Shopping ads give a complete picture of how your products are performing. You can track your product performance, filter how products are performing at the product, and analyze your metrics. You can also benchmark data, which gives you an idea of how your campaign is performing compared to your competitors.
How do Google Shopping Ads Work?
Shopping ads are automated based on the data sent to the search engines. To achieve that, you need to send the feed via a feed provider to the engine Merchant Center, linking your feed to the engine.
What’s a merchant center? Is an entity from a search engine that centralizes the information and helps manage shopping feeds. For example, you’ll need to create an account in Google’s merchant center before you can send your feeds to GoogleAds. To understand how all of this works, let’s go over the process of creating a Google Shopping Campaign.
How to Create a Google Shopping Campaign
Creating a Google Shopping campaign comprises a few simple steps:
1. Create your Google Ads account.
2. Create your Google Merchant account and link your Google ads account to it.
3. Set your product feed on the Google Merchant Center.
Add your product data, like product title, category, and price. Once you send the feed to Google Merchant Center, you can build campaigns in Google Ads.
How does the merchant center work? In Google or Microsoft, you submit your product data and create a feed according to certain specifications. There is a difference between Google and Microsoft merchant centers: while GMC is a separate entity and you need to create an account on it, on Microsoft the merchant center is under the Microsoft Ads user interface/ tools.
How do you send your feed to the Google or Microsoft Merchant Center?
You can send your product data to GMC in a couple of ways. If you have a few products, you can integrate Google Sheets directly with the GMC that will pull the product data from it automatically. If you have more than a few products, or you have a Shopify or BigCommerce e-store, there are apps in their system that automatically send feeds from your store to Google Merchant Center. Another option is to outsource with a third-party feed provider, but this means you still need to send your data to them first.
Once you choose how you’d send your feed, take care of any setting and admin areas in the Merchant Center. For instance, get your shipping, taxes, business information, and any other settings so you can start advertising your products right away.
4. Set up your campaign
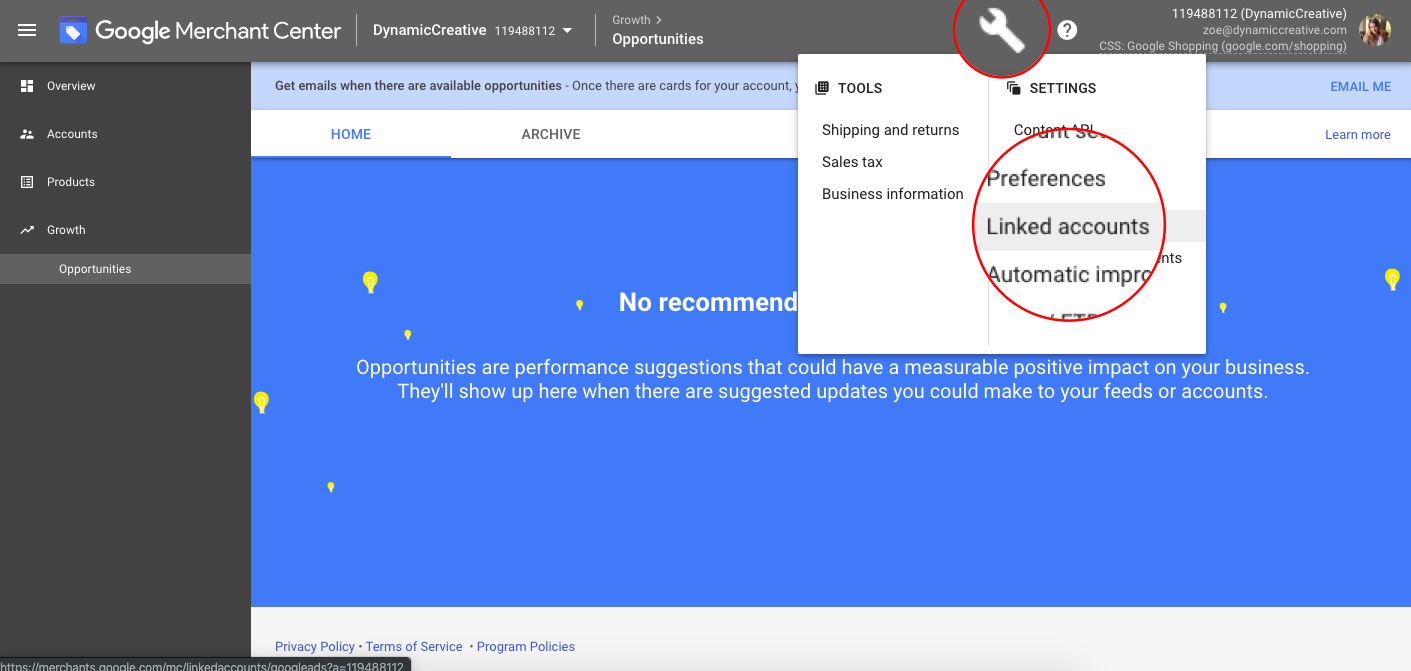
To create a campaign you first need to link your Google Ads account in the Google Merchant Center. To do that:
- Go to the Merchant Center
- Click the Tool icon and select “Linked Accounts”
- You’ll be requested to add your Google Ads Customer Identification Number (CID) and click send.
- Go to your Google Ads account. Select “Linked Accounts” You’ll see the Merchant Center Invite option.
- Accept the invite.
Building effective campaigns on Google or Microsoft Being is something for another article. Nevertheless, I’ll give you some tips to follow:
- Try multiple campaigns on your account so you can test the bidding and adjust the keywords for the right products.
- Look at how your customers search and base your bidding on the natural categories.
- Choose the main segment categories and then add them to campaigns. Then add segmented product categories into the ad groups.
Conversion tracking setup: Do this before creating your first campaign
Before setting your campaign, make sure you can track how effective your ads are. Setting up Conversion tracking helps you see how every click on your ad converts into customer activity on your website. By setting a conversion action you can track customer actions on your website and understand how clicks on your ads lead to sales and leads.
- From your Google Ads account select the Tools icon/ Measurement/ Conversions
- Click the plus button
- Click Website
- Select the type of action you want to track (Sales, Leads)
- Enter the name for the conversion you want to track on “Conversion name”
- Select a description for your conversion action
- In “Value”, choose how you want to track the value of each conversion. You can use the same value for all or assign different values to each conversion.
You can also choose how you want to count the conversions, how long you want to track them, and what to include in your “Conversions” column. Once you are finished with all the options click “Create and Continue” For more information about how to create a conversion tracking, see here.
Campaign creation: Standard Shopping vs Smart Shopping Campaigns
On Google, when you select Shopping as your campaign type, you can choose which type of campaign you want to run. There are two types of shopping campaigns you can run in Google: Standard Campaigns or Smart Campaigns:
Let’s compare both options:
| Standard Shopping Campaign | Smart Shopping Campaign | |
| Reach | Limited | Wide |
| Bidding | Manual and automated | Automated |
| Level of Control | High | Low |
| Optimization | High | Low |
| Remarketing | Optional | Included |
| Where will your ads appear? | Google Search Network | Search Network, Display Network, Search Partners, YouTube, Gmail |
| Transparency | High | Low |
| Best used for | New users | You want to automate your campaigns |
Standard campaigns offer more control and transparency. This means you can set the maximum CPC for each product. With Smart Shopping, all this process is automated. You are subject to the “Maximize Conversion Value” Strategy, which optimizes your CPC automatically.
How to Create a Bing Ads Shopping Campaign
Bing shopping campaigns are very similar to Google Shopping. There are a few differences though. For instance, instead of appearing at the top of the page, they appear in a grid format, on the right-hand side of the search results page.
How do you run Bing shopping ads?
If you are just coming to Bing Shopping, you need to create a Bing Merchant Center account:
- Go to your Bing Ads account
- Choose Tools / Bing Merchant Center / Create a Store
This will show Bing where your shopping catalog is stored. You’ll need to update the catalog at least every month.
How to create your Shopping Catalog
There are two main options to create your shopping catalog (also called feed):
- If you already have a Google Shopping feed, you can upload it as-is because it integrates with Bing.
- If you want to create a new catalog, you can do it as well. Here you can find the requirements for categories
To create a new feed:
- Select Tools/ Merchant Center/ Feeds from the top menu.
- Select Create Feed and enter your catalog name
- Choose your preferred options including country of sale and currency. Here’s help if you want to show your product in multiple countries.
- You will need to create a catalog file. You can do it in a spreadsheet or text file. Here is an example.
- Once created the catalog you need to submit it. You can manually upload files under 4MB, use an FTP/SFTP if your file is on-premises. If your file is online, you can download the file from the URL or download the feed file from Google Docs. Here you can find instructions on how to do it.
Here are some best practices to ensure your feed will work properly:
- Update the catalog at least once a month.
- Make sure the information, prices, description, and title are accurate.
- Use high-quality images that show the product clearly with a clear, solid background.
- Don’t leave any fields blank if possible. Here’s a table with required and recommended fields:
| Required fields | Recommended fields |
|
|
- Custom labels can help you create different product groups. For example, in the table below, you find some ideas for custom label metrics you can track and the values you can use to filter campaigns.
| Custom Label | Values |
| Popularity | High demand, low demand |
| Price range | High end, low end, sale |
| Stock level | Limited supply |
| Profit margin | High, low |
| Seasonal products | Winter, Summer, Holidays, Christmas |
Create your campaign
- Go to Create Campaign/ Sell Products from your account dashboard.
- Choose your settings, for example, priority level. This setting tells Bing which campaigns to prioritize. There are three priority options:
- High priority: This refers to focused campaigns, such as seasonal campaigns. When you choose this setting you are telling Bing to show these products first.
- Medium priority: Use this setting for products that perform well on a normal basis.
- Low priority: A sort of a catch-all campaign is the one Being will look on the last when choosing relevant products for a query.
Segmenting your ad groups
Once you create your campaign you can create your ad groups. Ad segmentation brings a lot of confusion to new users. Think of it as starting with a bucket containing all your ads. Then you divide the content into smaller buckets according to categories. For example, by brand, condition, any of your custom labels, product category, or type. You have a thousand ways to segment your ad groups in the way that best fits your account and campaign.
Ways to get your products into Shopping results
If you want to take advantage of Google Shopping and make sure your products show there are three routes you can take.
The first is simply aiming for organic search discovery. This means when a consumer type a product on Google and you hope your product will appear without needing paid promotion. Google calls this method Surfaces by Google and includes displaying a product in image results instead of text search results.
The second way available is the one we describe in this article, by using Shopping Ads through the Merchant Center. This allows you to set up shopping campaigns and view how the ads are performing.
The last option is a new experience which is called Google Shopping Actions. This marketplace is Google’s option to compete with Amazon and enables sellers to display their products on multiple google platforms including the Google Shopping mobile app and the Google assistant for mobile and even Google Home devices.
Tips to monetize your website with shopping ads
If you own a website, one of the best ways to earn extra revenue is by adding shopping ads to your digital property. How does it work? To put it simply, you partner with an advertising network (Like Google, Bing, or CodeFuel) and they display relevant ads on your website. Every time a viewer clicks on the ads, you get paid.
Ad networks usually pay publishers a rate per click, called Click-Through-Rate. For publishers, one of the most popular ad networks is Google AdSense. Check out our guide on How To Make Money With Google Adsense for more information.
To know more tips and strategies to monetize your website, check our Monetization Guide for Beginners in 2021 article.
How do shopping ads work on apps?
By showing your ads on mobile apps, you can reach a broader audience. How can you show your ads in apps in the Display Network?. Keep in mind that because of Google’s new rules, Google Ads no longer allows targeting app inventory via AdSense for mobile apps.
- On your Google Ads Account, select and click Display campaigns.
- Select Placements.
- Choose the ad group you want to show to apps.
- If you want to target a specific app category, choose from App categories.
- If you want to target specific apps, choose Apps, and search by name.
- You can also target multiple apps if you know their IDs by choosing to enter multiple placements then enter the IDs.
- Once you finish your selection, click Save.
If you don’t want the hassle, you can use an ad network or monetization platform that can automate your in-app advertising. If you are new to In-app advertising, check our complete guide In-app advertising: All you need to know and the best networks
5 Strategies to Maximize Revenue When Using Shopping Ads
To ensure you get the maximum revenue possible with shopping ads is not enough to create a perfect product feed and send it into the world. You also need to create and optimize your Google Shopping Campaign. Here are five tips you need to know to optimize your shopping campaign so you avoid wasting money on underperforming products.
1. Optimize your product feed
This should be where you start. By optimizing your product feed you are making it easier for Google to learn the information about your products. The more data they get about your products the better chance you have they are presenting them to your potential customers. Here are some tips to do it right:
- Optimize your images. Make sure you comply with Google’s rules and regulations. You can also conduct A/B testing to check what works best with your audience.
- Get the price right: Ensure Google is pulling the correct price, and in the right currency.
2. Optimize your campaign structure
This is another strategy that you can use for success. While you may not have a lot of control over your ads there are some things you can try. For instance, you can bid differently for different products. This will allow you to account for differences in profit margins, popularity and conversion rates.
Take advantage of the possibility of dividing your products into different groups. As we mentioned above you can divide them by category, brand, item ID, product type, and custom labels.
3. Find your weak spots
Normally, some of your products are going to perform better than others. By finding your “winners” and “losers” you can adjust your campaigns accordingly. The winners are the products that bring sales, the losers are the ones that albeit getting many visits, don’t get transactions.
You can find which ads are performing well and which aren’t by going to Reports/ View/Shopping.
4. Add negative keywords
You can limit the searches for which the ads will show by adding negative keywords. For example, if you sell silver jewelry, you may want to avoid people looking for gold jewelry. Thus you can add “gold” as a negative keyword. How do you do it?
- Go to Keywords
- Click on Details/ Search terms/ All
- Select the terms you want to use and add them as negative keywords.
5. Bid higher for selected search queries
This tip enables you to bid higher for the most valuable search queries. Here’s how to do it:
- Identify which search queries bring more value to your business.
- Create a copy of your current shopping campaign
- On one of the campaigns, you’ll exclude these queries and decrease the CPCs.
- Change the priority setting of this campaign to Low while the other is set to Medium. This is going to tell Google to pick the medium campaign thus enabling you to bid higher for better queries.
Shopping Ads Vs. Text Ads
Text ads and shopping ads often appear on the same search results page. Text ads are more flexible in terms of landing pages, ad copy, headlines, and keywords. Shopping ads, on the other hand, are more rigid in their structure. The following table highlights a comparison between the two ad types:
| Text Ad | Shopping Ad | |
| Destination URL | Landing page or product detail page | Product detail page |
| Character count limit | Three 30-character headline fields. Two 90-character description fields. | 70-character title field and up to 1000 character description field. |
| Avg. Click-through-rate | 3.17% | 0.86% |
| Extensions | Affiliate location, callouts, sitelinks, structured snippets, call, lead form, price, app, promotion, automated. | Price, promotion, local inventory, product ratings. |
Which ones should you use? You should use both. Text ads allow you to direct the customer to the landing pages. There is a significant value for brands that develop an integrated approach using both formats.
Shopping Ad FAQs
Where do shopping ads appear?
Shopping ads appear beyond Google’s SERP page. They appear on the Shopping tab, on search partner websites, on related sites like YouTube, on the Google Display Network, and the price comparison Shopping service.
What triggers shopping ads?
When a consumer is searching for a product, Google takes the relevant products from your product feed and shows them. That means you advertise based on product types.
Are shopping ads the same as display ads?
Shopping and text ads are based on keyword search. Display ads, on the other hand, display your visual ads beyond the search results page on an array of websites
How CodeFuel Optimizes the Performance of Shopping Ads
Optimizing your shopping ads can seem complicated, but CodeFuel simplifies and ensures high intent consumers are getting your ads. By basing our platform on contextual intent-based monetization, we encourage purchasing decisions from searches and increase conversions.
Learn more about how intent-based shopping ads optimize your campaigns and bring more revenue by contacting us.